Vitamin B9, popularly known as folate or folic acid, is one of eight vitamins that belong to the B-complex family. Like all B vitamins, B9 ensures proper adrenal function, maintains a healthy nervous system and regulates metabolic processes. Folate is naturally found in different types of food while folic acid is actually a synthesized form of folate.
Contents
The Basics of Vitamin B9
Folic acid is necessary for growth and development. It facilitates proper brain function and it plays a crucial role in emotional and mental health. It also assists in the production of the body’s genetic materials, RNA and DNA.

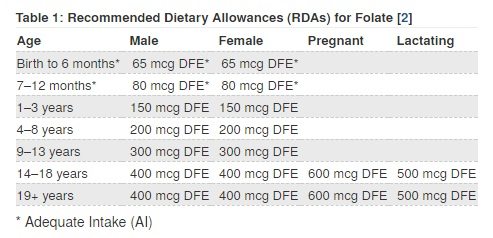
Medical experts believe that vitamin B9 is especially needed during these three stages: infancy, adolescence, and pregnancy. This is because it is during these times where body tissues and cells are growing rapidly.
Pregnant women are usually advised to get ample folic acid due to the following reasons:
- It support fetal and placental growth
- It helps prevent the occurrence of birth defects such as brain damage, spina bifida, and cleft palate.
Additionally, vitamin B9, together with vitamins B6 and B12, helps reduce the amount of homocysteine in the blood. Homocysteine is an amino acid which is implicated in increased risk of stroke and heart disease.
Why You Need More Folic Acid
Alcoholism, celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and pregnancy can all cause vitamin B9 deficiency. Symptoms are as follows:
- Depression
- Diarrhea
- Forgetfulness
- Gingivitis
- Irritability
- Loss of Appetite
- Low Birth Weight
- Mental Sluggishness
- Poor Growth
- Shortness of Breath
- Tongue Inflammation
Taking Too Much Vitamin B9
Too much of anything is bad, no matter how good that thing is. Very high doses of folic acid may cause confusion, gastrointestinal problems, nausea, loss of appetite, seizures, skin reactions, and sleep problems.
Sources of Vitamin B9
The following foods are rich sources of folate:
- Asparagus
- Avocado
- Beef liver
- Beets
- Brewer’s yeast
- Brussels sprouts
- Bulgur wheat
- Dark leafy greens
- Kidney beans
- Lima beans
- Milk
- Mung beans
- Mustard greens
- Orange juice
- Root vegetables
- Salmon
- Soybeans
- Spinach
- Turnips
- Wheat germ
- White beans
- Whole grains
You can download and print a large format version of our Vitamin B9 graphic here…
This is one of a series of posts on vitamins starting with vitamin A here…






